Personal Development, Business, Finance, and Investing for Everyone
An investment in knowledge always pays the best interest.
|
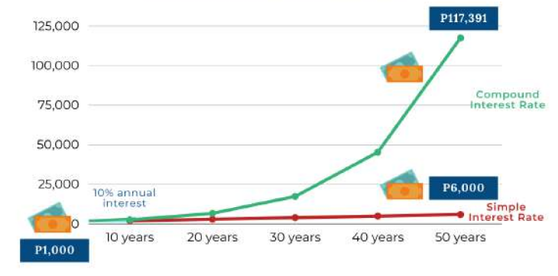
Why should interest, interest you? What is an Interest Rate? Interest Rate is the price paid for the use of money for some time, either fixed or variable. Interest Rate is the price paid for the use of money for some time, either fixed or variable. It can also be defined in two ways: Lending Rate It is the fee charged for lending money. Borrowing Rate It is the cost of borrowing money. Here in the Philippines, the interest rates are monitored by the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP). Lending Rate The range of interest (low to high) charged by financial institutions for lending money. The lowest rate of interest that a financial institution, such as a bank, charges is called the prime lending rate. Bank Average Lending Rate The weighted average interest rate (weighted average interest rate is the total interest on loans with different rates divided by total loan amount) charged by commercial banks on loans granted during a given period. Savings Deposit Rate Interest rate that a bank pays depositors for the use of their money for the period that the money is on deposit. Time Deposit Rate The interest rate that a financial institution pays depositors for interest-bearing deposits with fixed-maturity dates as evidenced by a certificate of deposit. Others, according to BSP: Treasury bill (T-bill) Rate Interbank Call Loan Rate Philippine Interbank Reference Rate (PHIREF) PHP BVAL Reference Rates BSP Bills Rate Overnight Lending Facility (OLF) Rate Overnight Deposit Facility (ODF) Rate Term Deposit Facility (TDF) Rate Overnight Reverse Repurchase (RRP) Rate Is Interest Rate a Friend or Foe? The reality is, it depends on whether you're earning it or paying it. Simple Vs. Compound Interest Rate While simple interest is interest on the principal amount only, compound interest is interest on interest. Compound interest is good for savings and investments but it can work against you in paying interest on loans. How are Interest Rates determined? Market rates are generally determined by supply and demand in the money market. Market-oriented Interest Rate Policy Since 1983, the level of interest rates is determined by the interaction of the supply and demand for funds in the money market. The BSP does not regulate the interest rate charged by banks, lending investors and pawnshops. The BSP only sets overnight rates, including the RRP rate, also known as the key policy rate. It is the interest rate at which the BSP borrows from banks to maintain price stability. Special Circumstances Under the BSP Charter, however, the BSP can impose/regulate interest rates as warranted under extraordinary economic and social conditions or crises. For example, on 24 Sep 2020, the BSP issued Circular No. 1098 which puts a ceiling on interest or finance charges from credit card transactions. The ceiling aims to ease the financial burden of consumers amid a challenging operating environment caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. Why doest the BSP allow the market to determine interest rates? The re-imposition of rate ceilings or limits may lead to distortions in the credit market.
What are the factors that influence the rise and fall of interest rates? Inflation Rate Annual percentage increase in the average price of the standard basket of goods and services consumed by a typical Filipino family for a given period. Lenders will demand higher interest rates as compensation for the decrease in purchasing power of the money they are paid in the future. Fiscal Policy Stance How the government's level of spending and taxation impact aggregate demand and economic growth. Intermediation Cost The cost incurred by financial institutions in extending their services. Included in the intermediation cost are administrative costs and the BSP's reserve requirements. Other Factors Those with longer-term maturity and with higher probability of incurring loss carry higher interest rates. Moreover, banks with larger holdings of non-performing assets (NPAs) are more cautious in their lending activities. This would tend to induce an increase in interest rates. How does Interest Rates affect consumers? Interest rates can either slow down or boost the economy. Importance of Interest Rates in the Economy Changes in interest rates can have both positive and negative effects on markets. How Interest Rates Affect Spending: The Impact of High Versus Low Interest Rates High Interest Rates can slow down the economy When interest rates are high, bank loans cost more, and consumers must cut back on spending. Businesses and farmers, for example, must cut back on spending for new equipment, thus slowing productivity, or reducing the number of employees. However, high interest rates encourage more people to save because they receive more on their savings. Demand falls and companies sell less. When there is less money circulating in the economy, the economy slows down. A Recession occurs when an economy contracts for two consecutive quarters. Low Interest Rates can boost the economy When interest rates fall, people and companies borrow more and save less. Output and productivity increase and boost economic growth.
If low interest rates provide so many benefits, why aren't they kept low all the time? Having very low interest rates for a long time can cause Inflation.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
PLACE YOUR ADS HERE YOUR PAYDAY REMINDER FEATURED PARTNER FEATURED PROMOTIONS FEATURED MENTIONS PLACE YOUR ADS HERE PLACE YOUR ADS HERE For more updates about Personal Development, Financial and Investment Education. Join and Subscribe to my Newsletter. It's FREE! ABOUT THE BLOGGERHi, I'm Ralph Gregore Masalihit! An RFP Graduate (Registered Financial Planner Institute - Philippines). A Personal Finance Advocate. An I.T. by Profession. An Investor. Business Minded. An Introvert. A Photography Enthusiast. A Travel and Personal Finance Blogger (Lakbay Diwa and Kuripot Pinoy). Currently, I'm working my way toward time and financial freedom. PLACE YOUR ADS HERE Follow me on |